Visual Studio 2013 Lesson 18: The Math Functions
[Lesson 17] << [Contents] >>[Lesson 19]
18.1 The Abs function
The Abs function returns the absolute value
of a given number.
The syntax is
Math. Abs (number)
* The Math keyword here indicates that the Abs function belong to the Math class. However, not all mathematical functions belong to the Math class.
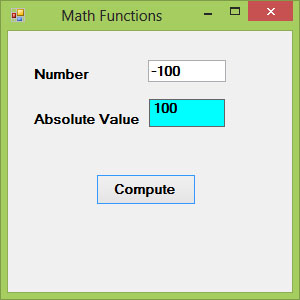
Example 18.1
In this example, we shall add a text box control for the user to input his or her number and a label control to display the absolute value of the number. We need to use the Val function to convert text to numeric value. Rename the textbox as TxtNum and the label as LblAbs.
The Code
Private Sub BtnComp_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnComp.Click
LblAbs.Text = Math.Abs(Val(TxtNum.Text))
End Sub
The output
18.2 The Exp function
The Exp function returns the exponential value of a given number. For example, Exp(1)=e=2.71828182
The syntax is
Math.Exp (number)
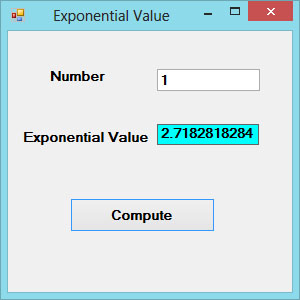
Example 18.2
In this example, we shall add a text box control for the user to input his or her number and a label control to display the exponential value of the number. Rename the textbox as TxtNum and the label as LblAbs.
The Code
Private Sub BtnComp_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnComp.Click
LblExp.Text = Math.Exp(Val(TxtNum.Text))
End Sub
The Output
Figure 18.2
18.3 The Fix Function
The Fix function truncates the decimal part of a positive number and returns the largest integer smaller than the number. However, when the number is negative, it returns the smallest integer larger than the number. Fix does not belong to the Math class therefore we do not use the Math keyword.
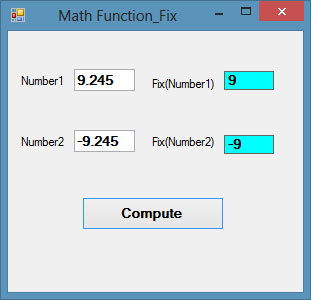
Example 18.3
Private Sub BtnComp_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnComp.Click
LblFixNum1.Text = Fix(Val(TxtPosNum.Text))
LblFixNum2.Text = Fix(Val(TxtNegNum.Text))
End Sub
The Output
Figure 18.3
18.4 The Int Function
The Int is a function that converts a number into an integer by truncating its decimal part and the resulting integer is the largest integer that is smaller than he number. For example
Int(2.4)=2, Int(6.9)=6 , Int(-5.7)=-6, Int(-99.8)=-100
18.5 The Log Function
The Log function is the function that returns the natural logarithm of a number.
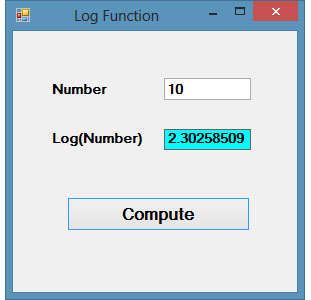
Example 18.4
Private Sub BtnComp_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnComp.Click
LblLog.Text = Math.Log(Val(TxtNum.Text))
End Sub
The Output
Figure 18.4
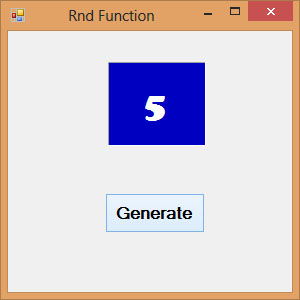
18.6 The Rnd( ) Function
Rnd is a very useful function in Visual Studio 2013 . We use the Rnd funciton to write code that involves chance and probability. The Rnd function returns a random value between 0 and 1. Random numbers in their original form are not very useful in programming until we convert them to integers. For example, if we need to obtain a random output of 6 integers ranging from 1 to 6, which makes the program behave like a virtual dice, we need to convert the random numbers to integers using the formula Int(Rnd*6)+1.
Example 18.5
Private Sub BtnGen_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnGen.Click
LblRnd.Text = Int(VBMath.Rnd() * 6) + 1
End Sub
Notice that the Rnd() function belongs to the VBMath class in Visual Studio 2013 . This is different from Visual Basic 2012, where you can omit the VBMath keyword.
In this example, Int(Rnd*6) will generate a random integer between 0 and 5 because the function Int truncates the decimal part of the random number and returns an integer. After adding 1, you will get a random number between 1 and 6 every time you click the command button. For example, let say the random number generated is 0.98, after multiplying it by 6, it becomes 5.88, and using the integer function Int(5.88) will convert the number to 5; and after adding 1 you will get 6.
The Output
Figure 18.5
*We shall learn how to create an animated dice using a Timer control in later lesson
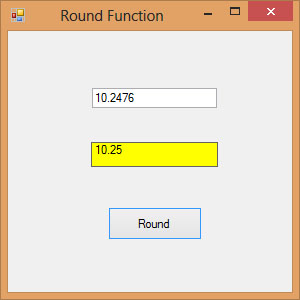
18.7 The Round Function
The Round function is the function that rounds up a number to a certain number of decimal places. The Format is Round (n, m) which means to round a number n to m decimal places. For example, Math.Round (7.2567, 2) =7.26
Example 18.6
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Label1.Text = Math.Round(Val(TextBox1.Text), 2)
End Sub
The Output
Figure 18.6